How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to legal regulations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone operation, ensuring you gain the confidence and knowledge to fly responsibly and enjoyably.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the practical knowledge and theoretical understanding necessary to become a proficient drone pilot. We’ll delve into the details of flight controls, maintenance, and legal considerations, making your journey into the world of drone piloting smooth and successful.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the individual components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key parts of a typical drone, provides a glossary of common terms, and illustrates their interconnections.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. These include the propellers, motors, electronic speed controllers (ESCs), flight controller, battery, GPS module, and the camera (if equipped).
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, fly, and maneuver. Failure points include damage from impacts or wear and tear.
- Motors: Electric motors convert electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to spin the propellers. Overheating or bearing failure are common issues.
- Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs): These regulate the speed of each motor, allowing for precise control of the drone’s movement. ESCs can fail due to overheating or electrical damage.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” processing data from various sensors (like gyroscopes, accelerometers, and GPS) to maintain stability and execute commands from the controller. Malfunctions can lead to erratic flight or complete system failure.
- Battery: This provides the power for all drone components. Over-discharging, damage, or age can significantly impact flight time and performance.
- GPS Module (if equipped): This enables the drone to determine its location and maintain its position, crucial for features like GPS mode and Return-to-Home (RTH).
- Camera (if equipped): This captures photos and videos. Common issues include lens damage, malfunctioning image sensors, and gimbal problems.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology is essential for understanding manuals, troubleshooting issues, and communicating effectively with other drone pilots.
| Term | Definition | Term | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude Hold | Maintains a constant altitude. | Gimbal | A stabilized mount for the camera. |
| Atti Mode | Attitude mode; relies on onboard sensors for stabilization, not GPS. | GPS Mode | Uses GPS for position and altitude holding. |
| ESC | Electronic Speed Controller. | Payload | Anything carried by the drone (camera, sensors, etc.). |
| Firmware | Software that controls the drone’s hardware. | Return-to-Home (RTH) | Automated return to the takeoff point. |
| Flight Controller | The central processing unit of the drone. | Throttle | Controls the drone’s vertical speed (up/down). |
Drone Component Diagram

A labeled diagram would show the interconnections between the battery, flight controller, ESCs, motors, and propellers. The flight controller receives input from sensors and the remote controller, processing this data to send commands to the ESCs, which in turn control the motors and propellers. The battery powers the entire system. Each component’s potential failure points, as detailed above, should be indicated visually on the diagram.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety guidelines are paramount for safe and responsible drone operation. This section Artikels essential steps to ensure a successful and hazard-free flight.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, diligently follow this checklist to minimize the risk of accidents or malfunctions.
- Check battery charge level and ensure it is adequately charged.
- Inspect propellers for any damage or cracks. Replace if necessary.
- Verify GPS signal strength and accuracy.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Check all connections and ensure all components are securely attached.
- Review the flight plan and identify potential hazards in the flight area.
- Ensure you have all necessary permits and are operating within legal limits.
Safety Guidelines and Risk Assessment
Safety should be your top priority. Always operate your drone responsibly, respecting legal regulations, airspace restrictions, and the safety of others. Conduct a thorough risk assessment before each flight, considering factors such as weather conditions, nearby obstacles, and potential hazards.
- Legal Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local, regional, and national drone regulations. These often include airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations.
- Airspace Restrictions: Avoid flying near airports, heliports, and other restricted airspace. Use online resources to check airspace restrictions before each flight.
- Emergency Procedures: Know how to perform an emergency landing in case of a malfunction or loss of control. Practice emergency procedures in a safe environment.
- Risk Mitigation: Identify potential hazards before each flight and develop strategies to mitigate these risks. For example, choosing a less windy day, avoiding crowded areas, and having a spotter to assist.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoffs and landings are fundamental to responsible drone operation. This section details the procedures for various scenarios.
Safe Takeoff Procedure, How to operate a drone
A safe takeoff involves careful calibration and selection of a suitable location. Begin by calibrating the drone’s compass and IMU. Select a level, open area away from obstacles and people. Ensure the propellers are clear and the GPS signal is strong. Slowly increase the throttle to initiate lift-off, maintaining a steady ascent.
Safe Landing Procedure
A smooth landing requires careful maneuvering and consideration of wind conditions and obstacles. Begin by slowly descending, maintaining a steady rate of descent. Once close to the ground, reduce the throttle gradually to a gentle touchdown. Avoid sudden movements or harsh landings.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Different drone models and environments may require variations in takeoff and landing techniques. For example, in windy conditions, you may need to adjust your approach to compensate for wind gusts. Some drones offer assisted takeoff and landing features, simplifying the process. Always consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is essential for safe and effective drone operation. This section explains the functions of control sticks and how to perform fundamental maneuvers.
Drone Controller Functions
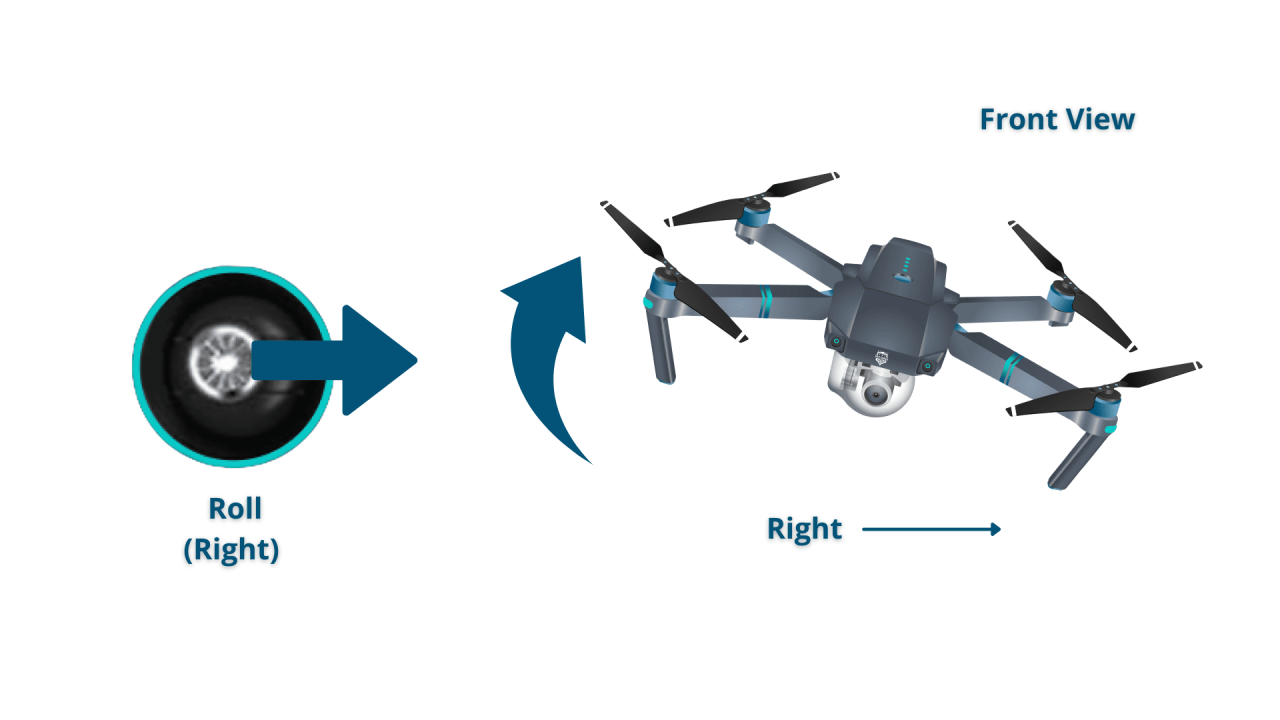
A typical drone controller has two control sticks. One stick typically controls altitude (throttle) and yaw (rotation), while the other controls roll (tilt left/right) and pitch (tilt forward/backward). Understanding the relationship between stick movements and drone response is key to successful flight.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Mastering basic maneuvers is crucial for building confidence and control. These include hovering (maintaining a steady position in the air), ascending (moving upwards), descending (moving downwards), moving forward/backward/left/right, and rotating (yawing).
Flight Control Practice Exercises
Practice is essential for developing proficiency. Start with simple maneuvers like hovering in a safe, open area. Gradually increase the complexity of your maneuvers as your skills improve. Practice transitions between maneuvers smoothly. Consider practicing in a simulator before flying your actual drone.
Advanced Flight Techniques
This section explores advanced flight modes and techniques for navigating challenging conditions and utilizing automated features.
Advanced Flight Modes
Many drones offer advanced flight modes such as GPS mode (relies on GPS for stability and position holding), Atti mode (attitude mode, relies on onboard sensors), and Sport mode (allows for more aggressive and responsive maneuvers). Each mode has advantages and disadvantages depending on the flight conditions and pilot’s skill level. GPS mode is generally safer for beginners, while Atti mode provides greater agility but requires more skill.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of safety regulations and best practices. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including legal requirements and practical tips, please refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently and safely operate your drone.
Challenging Flight Conditions
Flying in strong winds or confined spaces requires advanced techniques. In windy conditions, you may need to adjust your flight path and compensate for wind gusts. In confined spaces, precise control and awareness of surroundings are crucial. Practice these techniques in a safe and controlled environment before attempting them in real-world scenarios.
Waypoint Navigation and Automated Features
Many drones offer waypoint navigation, allowing you to plan a flight path in advance. This is particularly useful for complex aerial photography or surveying tasks. Automated features such as Return-to-Home (RTH) can help ensure the safe return of the drone in case of signal loss or other emergencies.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section details how to achieve professional-looking aerial shots.
Camera Settings Adjustment
Adjusting camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is crucial for achieving optimal image quality. Higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions, but can introduce noise. Shutter speed affects motion blur, while aperture controls depth of field.
Camera Angles and Shots
Experiment with different camera angles and shots to create visually appealing content. Examples include:
- Aerial panoramas: Capture wide, sweeping views of landscapes.
- Cinematic sequences: Create dynamic and engaging video footage.
- Close-up shots: Highlight details and textures.
- Tracking shots: Follow subjects as they move.
Composition and Storytelling
Effective aerial photography and videography involves more than just technical skill. Consider composition techniques like the rule of thirds and leading lines to create visually appealing images. Use camera angles and movement to tell a story and convey a message.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued reliable operation.
Regular Maintenance Schedule

A regular maintenance schedule should include cleaning the drone body and propellers, inspecting for damage, checking battery health, and updating firmware. Proper storage is also crucial to protect the drone from damage and extend its lifespan.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, damaged power switch | Charge battery, replace battery, inspect power switch | Regularly check battery level, handle with care |
| GPS signal lost | Obstructed signal, weak signal, faulty GPS module | Move to an open area, check for interference, replace GPS module | Fly in open areas, avoid interference |
| Propeller malfunction | Damaged propellers, loose propellers | Replace damaged propellers, tighten propellers | Regularly inspect propellers |
| Erratic flight | Faulty flight controller, low battery, software issues | Calibrate flight controller, replace battery, update firmware | Regular calibration, check battery levels, update firmware regularly |
Proper Drone Storage
Store your drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Keep the battery separate and store it at an appropriate charge level to prevent damage.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and adhering to drone regulations is crucial for responsible and legal operation. This section Artikels key regulations and procedures.
Drone Regulations by Jurisdiction
Drone regulations vary by location. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific rules and regulations in your area, including airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations.
| Jurisdiction | Regulations | Jurisdiction | Regulations |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Example: USA – FAA] | [Example: Registration requirements, airspace restrictions] | [Example: UK – CAA] | [Example: Operational limits, permit requirements] |
| [Example: Canada – Transport Canada] | [Example: Flight restrictions, pilot certification] | [Example: Australia – CASA] | [Example: Operational standards, safety guidelines] |
Permit and License Acquisition
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses to operate a drone. Check with your local aviation authority to determine any necessary requirements.
Penalties for Violations
Violating drone regulations can result in penalties, including fines, suspension of flight privileges, and even criminal charges. Always prioritize safe and legal operation.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding experience that combines technical skill with a keen understanding of safety and regulations. From the initial thrill of takeoff to the creative possibilities of aerial photography, this guide has provided a solid foundation for your drone piloting journey. Remember to always prioritize safety, practice regularly, and continue to expand your knowledge – the skies await!
Question & Answer Hub: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes. Look for models with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, weather conditions, and flight style. Expect anywhere from 15-30 minutes on a single charge for many consumer drones.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Most drones have fail-safe mechanisms, often reverting to “Atti” mode (attitude stabilization) allowing for controlled flight based on the drone’s internal sensors. However, immediate landing is recommended.
Do I need insurance for my drone?
Drone insurance is highly recommended, especially for commercial use, to cover potential damage or injury caused during operation.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures.